9 Minutes
CONTENTS
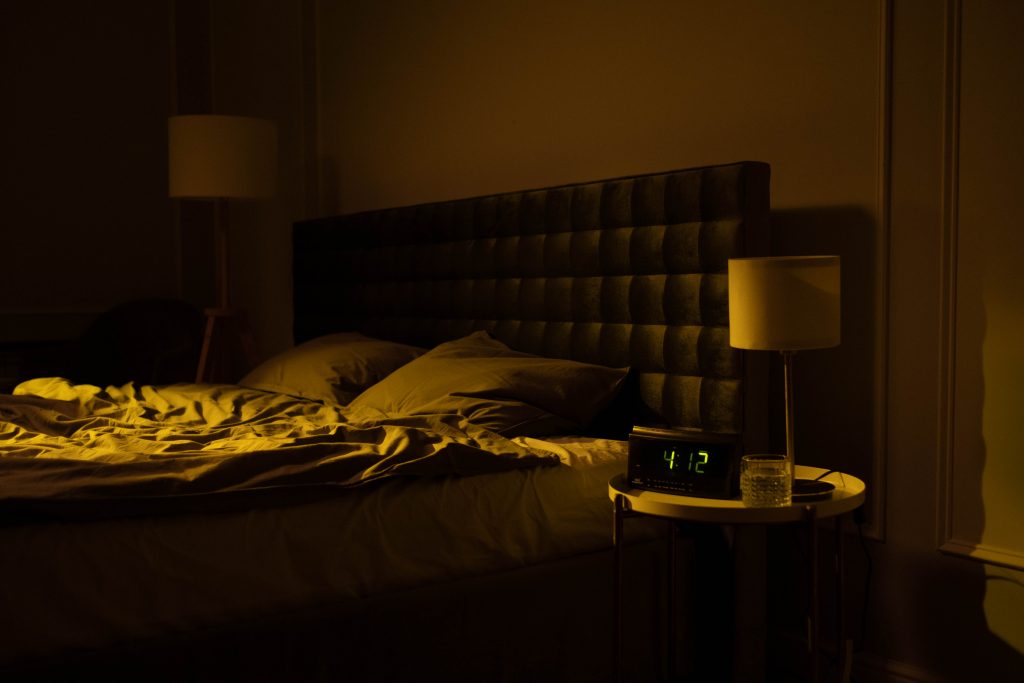
It’s past midnight, and you lie in bed with your eyes wide awake. As the clock keeps ticking, you toss and turn but fail to fall asleep no matter how hard you try. You may feel like you are cursed, but know that you are not alone in this struggle. Experts estimate that between 30 to 40 percent of adults across the world struggle with some degree of insomnia, a condition which makes it difficult to fall or stay asleep at night. Women, in particular, have a lifelong risk of insomnia which is around 40 per cent more than men.
There can be multiple reasons your brain isn’t letting you rest at night. The reason can be anything from a stressful event, such as getting fired from a job, or a long-term health issue, like depression. Regardless of the causative factor, it is important to remember that the initial brief periods of insomnia you develop occasionally can turn into a long-term issue if you do not seek help.
With the recent advances in modern science, you no longer need to suffer from this debilitating health issue. Multiple therapies, medications, and simple lifestyle changes are now available to retrain your mind and body and get the sleep you need to stay healthy and happy.
This article will help you learn how to treat insomnia using different medical and non-medical ways.

FAQs
A UNIQUE METHOD TREATING Sleep
a successful and proven concept focusing on underlying causesSleep TREATMENT LASTING APPROACH
0 Before
Send Admission Request
0 Before
Define Treatment Goals
1 week
Assessments & Detox
1-4 week
Psychological & Holistic Therapy
4 week
Family Therapy
5-8 week
Aftercare
12+ week
Refresher Visit
Sleep Insights
latest news & research on Sleep
Chronic Insomnia Treatment
At luxury treatment centers, MBIs are often combined with other evidence-based treatments for chronic insomnia, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
read more
Sleep Deprivation Hallucinations
Sleep deprivation and hallucinations are interconnected phenomena that highlight the intricate relationship between sleep quality and cognitive function
read more